Capabilities:
- High sensitivity point scanning confocal imaging
- Spectral array GaAsP detectors
- Inverted microscope
- Incubation for live cell timelapse - temp and CO2 control
- Definite focus for timelapse
Power Up
- Turn on Main Switch
- Turn on the X-Cite (if you need to see fluorescence down the eyepieces)
- Turn on System PC switch
- Turn on the components switch
- Turn the key to position 1 on the Lasos Argon laser (large black box) if you will use it.
- Check to see if the argon laser is set to "Run" not "idle"
- Turn on the PC
OR
- If the system is left on for you check the Argon laser is in run mode.
If using the environmental controls, press the "Incubation" button on the touch pad. Set and activate the needed controls: the stage insert ("H Insert P"), the stage insert cover ("Inc PM"), the humidifier ("H Dev"), or the CO2 regulator ("CO2 Small V").
Logging ON and Starting the Software
- Select the "LMCFuser" account and enter the password
- Double-click the ZEN Black 2011 Imaging icon on the desktop and choose "Start System" when the boot status window pops up
Go to the Locate tab, click online and choose the means of viewing - Brightfield, Blue, Green or Red fluorescence
Click "RL Illumination Off" on the touch pad or the shutter off button to turn off fluorescence (if you just use BF leave it on so the system automatically turns that on each time you go to ocular)
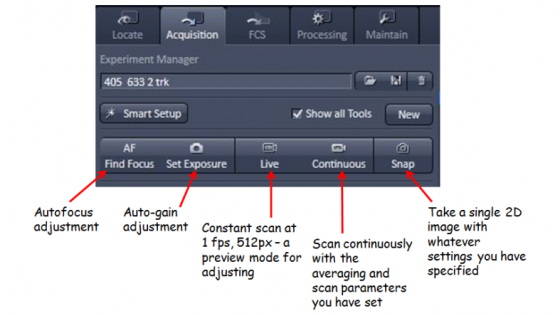
Click the "Acquisition" tab so you see all the settings for confocal imaging. If the "Show manual tools" box is unchecked some of the less common adjustments are hidden (the Show all check marks on each blue bar gives a similar option).
Setup
If you follow the smart setup path . . .
However, the smart setup path does NOT necessarily assign the fluorophores chosen to the optimal detector for the emission wavelength of the chosen fluors. Specifically, fluors with wavelengths in the middle of the visible light spectrum may NOT be assigned to the higher sensitivity GaAsP detector.
Manual setup
Or you can manually change the excitation lasers, emission bands, dichroics etc in the Imaging Setup and Light Path tabs.
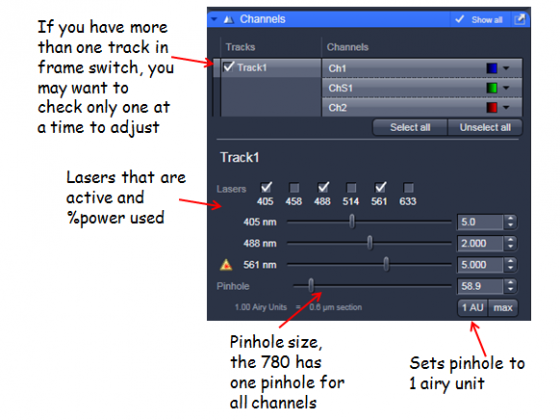
- The MBS (Main Beam Splitter = dichroic) needs to match the lasers used in the visible and 405 light paths)
- One track for simultaneous imaging of the channels, more than one track for sequential scanning
- For multi-track: Frame switching should be used if different dichroics, pinholes or overlapping emission bands are required. Line switching is more convenient and possible when only electronic things change between tracks (eg AOTF control of excitation, which detector is active)
- Ch1 and Ch2 are standard alkali PMTs, ChS1 is an array of 32 high-sensitivity GaAsP PMTs. This can be used as up to 8 channels in Channel mode (but they have to have the same gain at any time, but different digital gain is allowed).
- If you have created a configuration you can save this for easy reloading in the future
- Please ask if you need some help to design an optimal setup for your particular fluorophores and experiment.
Pressing Auto-Exposure is a good starting point to get an image on the screen to optimize. Auto-exposure changes the detector gain values so something is visible.
Live (this was called FastXY in the 510 software) constantly scans quite quickly at a fairly low resolution to allow you to make adjustments. (If you need to have the scan parameters you will subsequently adjust to be in effect you can press continuous).
Adjust the z-position with the coarse/fine focus knob (notice these are on the touch screen pad as well as the microscope) to choose the plane of interest. If you are taking a z-stack generally choose the brightest plane to adjust the settings.
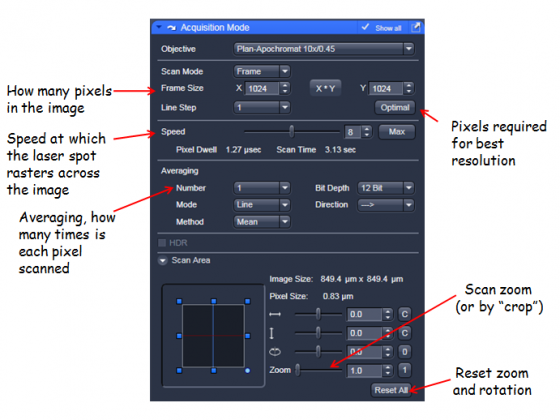
Zoom - you can do this with the "Crop" button underneath the image - resize the box that appears - or using the scan area controls in the Acquisition Mode panel.
Laser powers - adjust the sliders (note the are non-linear) so you have reasonable excitation. The lowest value you can get away is best to minimize fluorophore saturation and photodamage.
Pinhole - adjust so a suitable optical slice is obtained. A trade-off between z-axis resolution and brightness. A pinhole of one Airy unit gives essentially gives you the best resolution, opening it slightly from there will allow you to collect more signal.
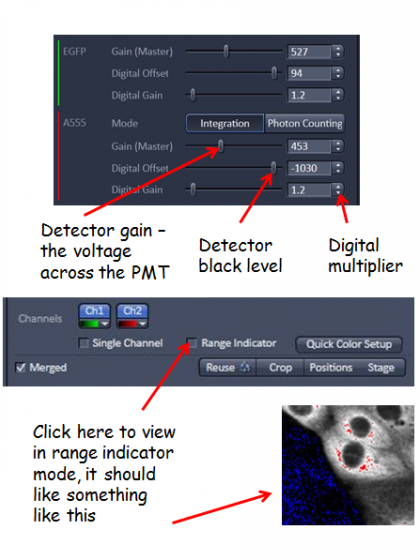
Gain/offset optimization - adjust the gain (detector sensitivity) and offset (background level) for each channel. Selecting range indicator is helpful when doing this. In this mode saturated pixels are highlighted red and 0 intensity blue, a few red pixels and the background 50% blue is often a good point to aim for. VERY IMPORTANT: the gain levels for the GaAsP detectors (ChS1, ChS2,...) should be set between the range of 600-800 volts, the linear range of the detector. If you have a good image with a gain below 600 volts, then adjust the laser power down to minimize your photobleaching/phototoxicity to your sample. Conversely, if you need to adjust the gain on these detectors abouve 800 volts, reduce the gain back into the range and raise the digital gain to increase the image intensity.
Averaging and scan speed - Averaging and slower scan rates improve SNR, choose a good balance for quality and speed.
Sampling rate - The number of pixels in the image can be selected. The optimal button selects the correct number for a particular objective, wavelength and zoom. This will give you a digital sampling rate adequate to fully sample the optical resolution.
The acquisition Mode panel also allows you to adjust between unidirectional and bidirectional scanning (faster but sometimes causes image degradation), and the bit depth of the images (8bit is fine for standard imaging, 12-bit may help with some quantification).
Press the Snap button to acquire an image with the settings you have specified above.
Click the disk icon beneath the open images icons to save the selected image as .lsm files. Generally it is best to save to the D:/ drive and move the data to a server, USB drive etc after you have closed the software.
The software creates a new tab in most but not all acquisition cases so save as you go to avoid loosing anything.
The LSM image format can be open by the free offline viewer or FIJI/ImageJ. You can export images as TIFF from the File\Export menu.
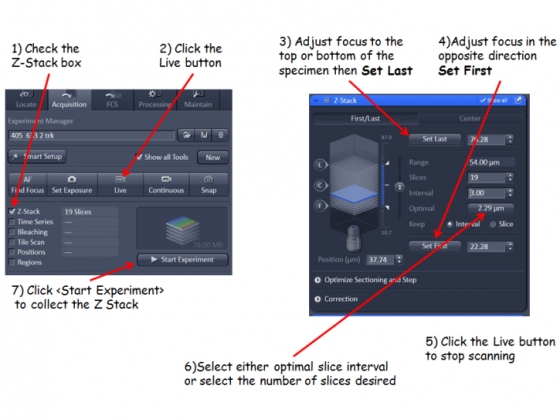
- Select the Time Series box underneath the Z-series box of above
- Choose the number of time points and the interval between them
- Press start experiment
And of course you can do a time series of a stack by having both things active. You will end up with a 4D dataset that can be saved as a single .LSM file.
- Remove sample and clean any immersion objectives that you used
- Move your saved data as appropriate
- Record your use of the system using the CoreResearch booking system
If the next user is scheduled within thirty minutes ofthe end of your session:
- Close the Zen2011 software
If the next user is scheduled within 2 hr, but more than thirty minutes from the end of your session:
- Close the Zen2011 software
- Flick the small switch on Lasos controller board to standby.
If nobody is scheduled to use the confocal after you:
- Turn key on Lasos black box (5) to 0 position and wait for about 3-5 min until fan shuts off.
- In the meantime, exit Zen2011 software and shut down PC from the Windows Start Menu
- Turn off System PC and components switches after the cooling fan from 1 is quiet. (3 & 4)
- Turn off Main Switch (2)
- Turn off X-Cite (1)
- Cover the microscope